Unbelievable Info About How To Treat Respiratory Alkalosis

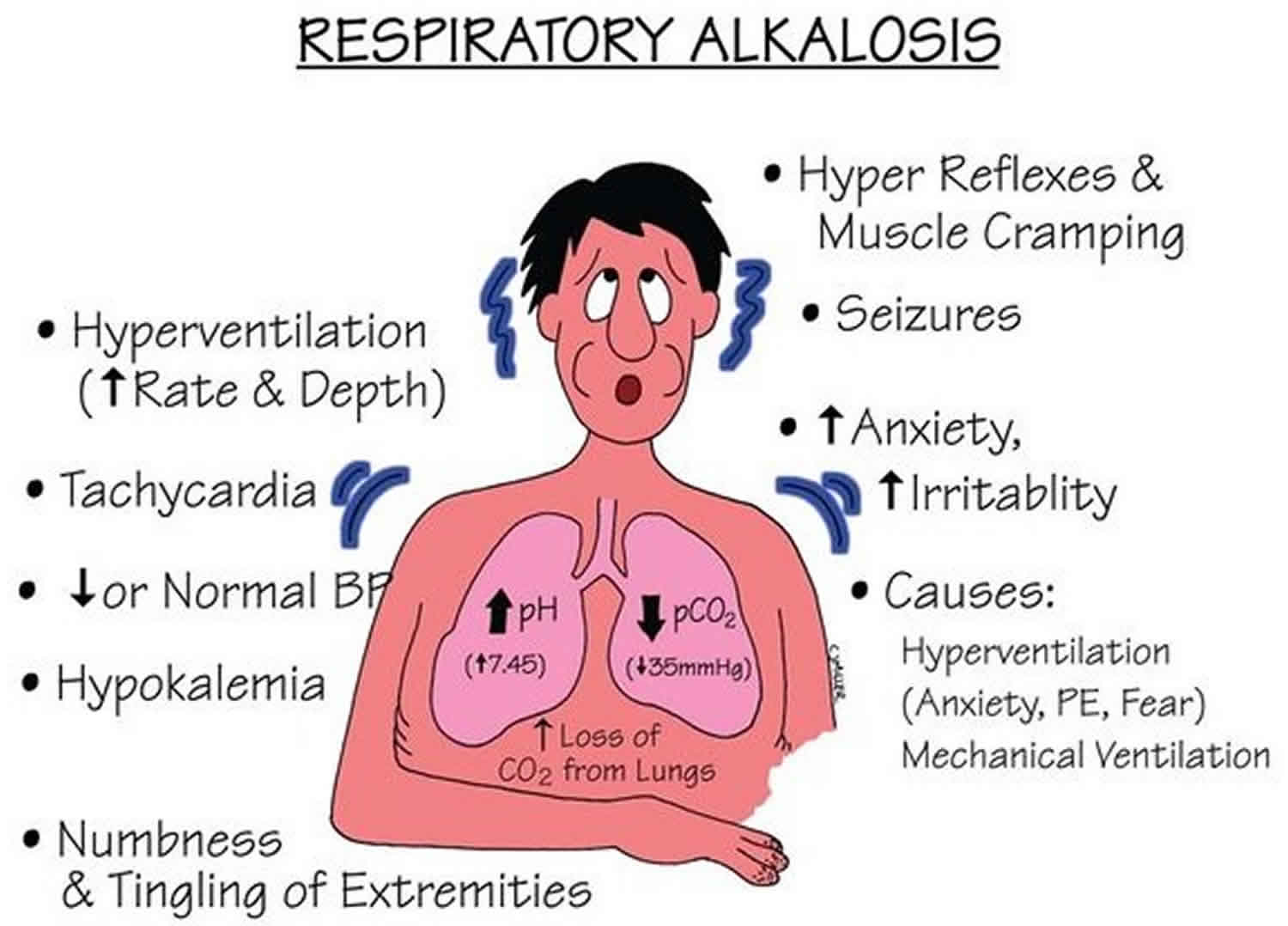
Respiratory alkalosis is a pathology that is secondary to hyperventilation.
How to treat respiratory alkalosis. In pregnancy, progesterone stimulates the respiratory center, producing an average pco 2 of 30 mm hg and respiratory alkalosis. Features of hypocalcemia (alkalemia reduces ionized calcium level): Administration of oxygen to those with hypoxemia or returning the patient to lower altitudes can reverse.
Supplementary content textbook presentation the presentation of respiratory alkalosis depends on the underlying disorder. Hyperventilation typically occurs in response to an insult such as hypoxia, metabolic acidosis, pain, anxiety, or increased metabolic demand. Treatment treatment is aimed at the condition that causes respiratory alkalosis.
Alkalosis is moderate to severe (either causing symptoms). Treatment outlook prevention what is respiratory alkalosis? Management of respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory alkalosis occurs when the levels of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood aren’t balanced. The treatment of respiratory alkalosis is primarily directed at correcting the underlying disorder. It results from the lungs getting rid of too much carbon dioxide through increased breathing.
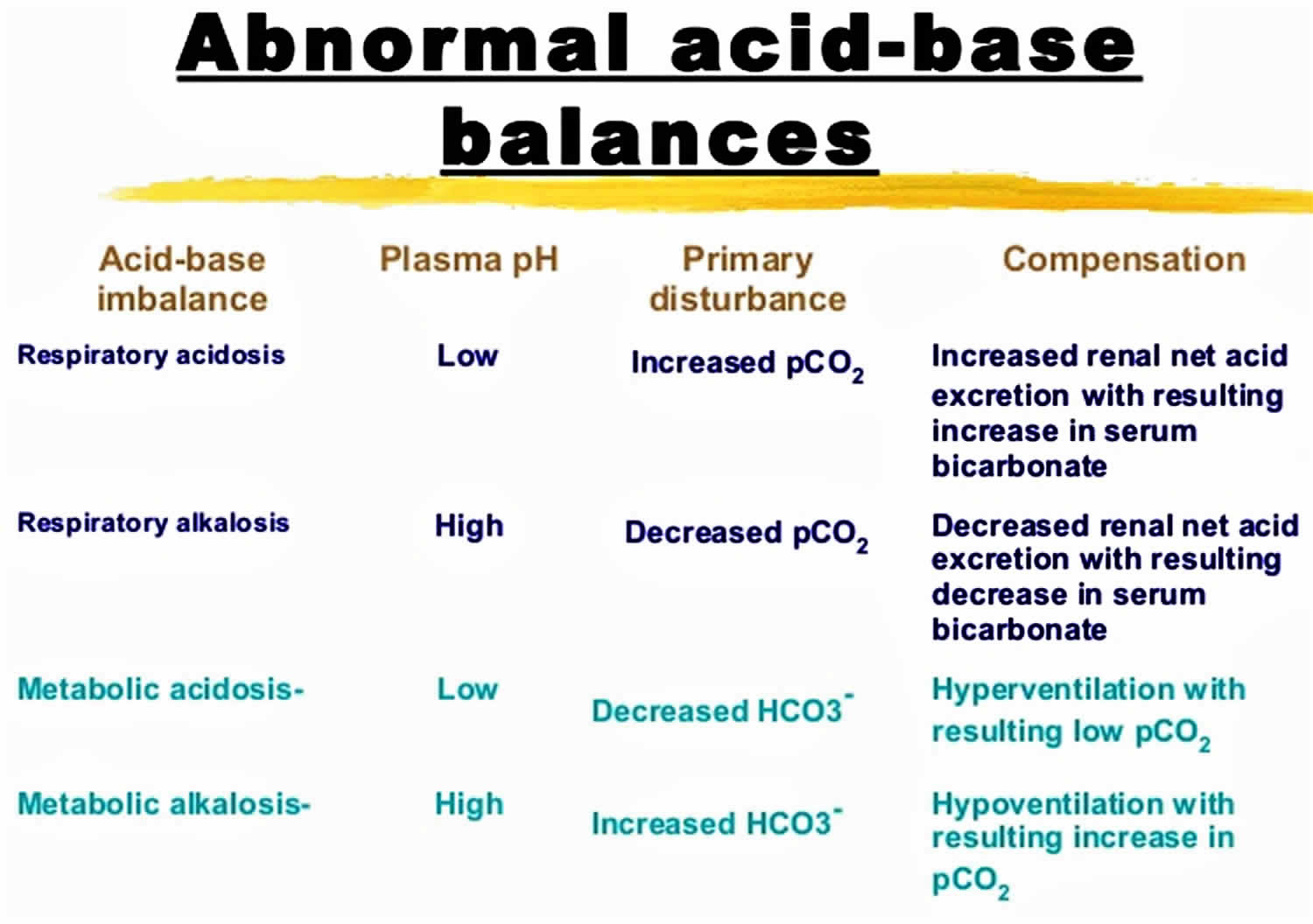
Treatment key points respiratory alkalosis is a primary decrease in carbon dioxide partial pressure (p co2) with or without compensatory decrease in bicarbonate (hco 3− ); However, the underlying etiology may be. The treatment of primary respiratory alkalosis begins with addressing the underlying cause when possible.
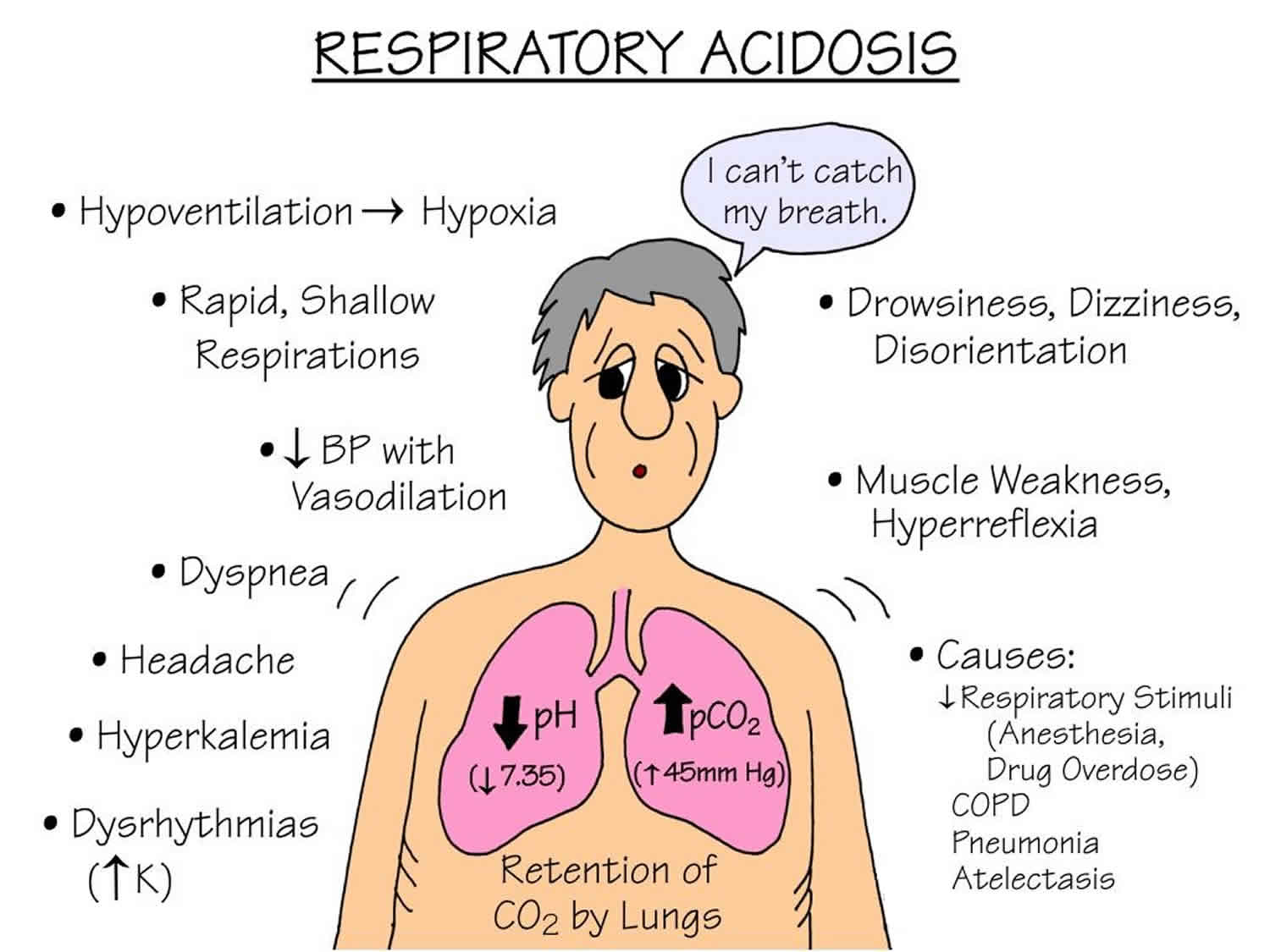
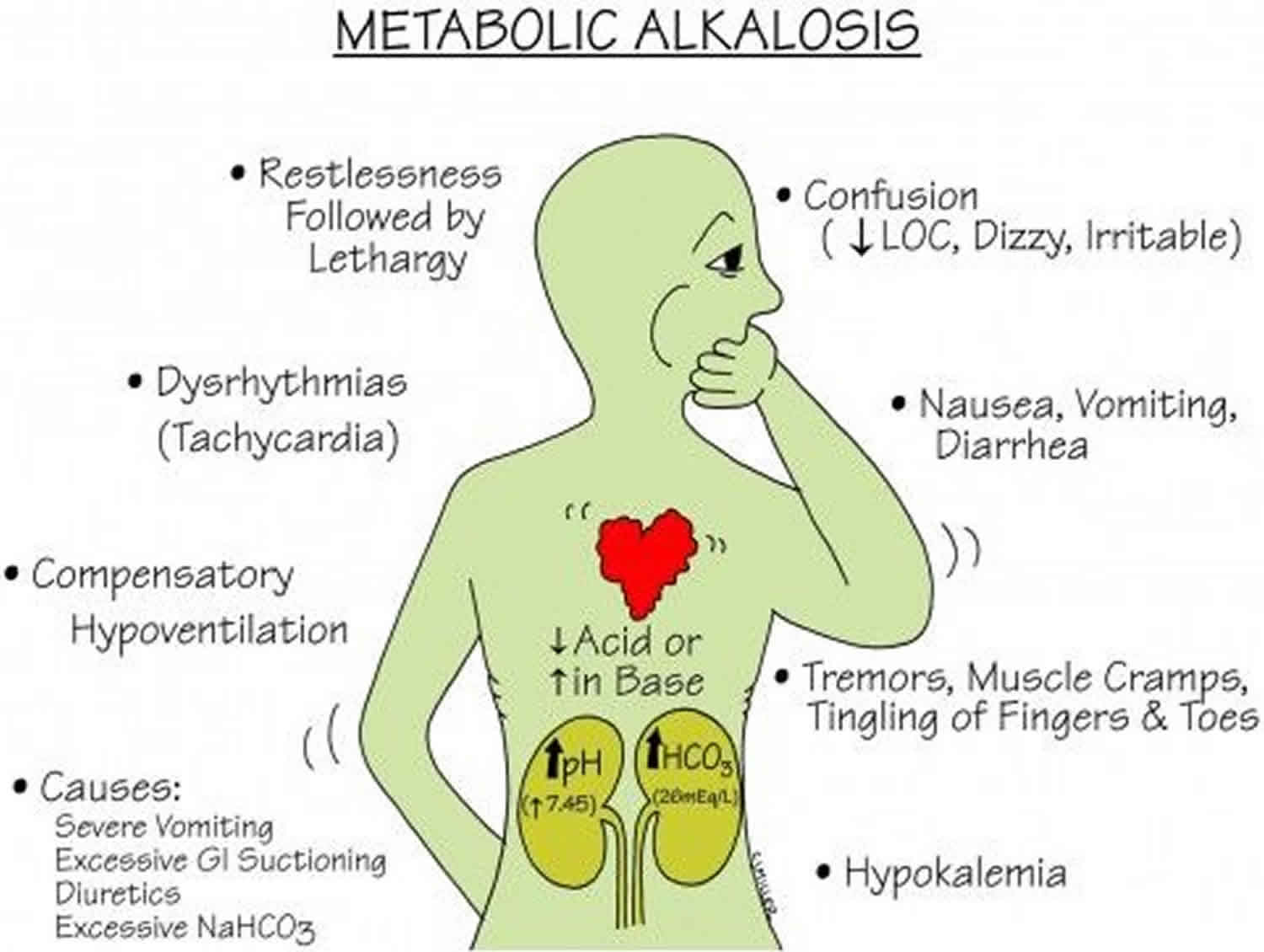
Respiratory acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. Two factors are required for the genesis and then maintenance of metabolic alkalosis: This activity reviews the evaluation and management of alkalosis and highlights the interprofessional team's role in improving care for patients with alkalosis.
Most causes are associated with tachypnea, which can be dramatic or subtle. Paresthesias of extremities and mouth. Respiratory alkalosis itself is rarely life threatening.
Salicylates directly stimulate respiration and aspirin toxicity should be suspected when both. Disease highlights hyperventilation induces hypocapnia causing respiratory alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis can be acute or chronic.
Chronic respiratory alkalosis typically has no symptoms. A process that raises the plasma bicarbonate concentration and a process that prevents excretion of the excess bicarbonate in the urine [ 1,2 ]. Salicylates directly stimulate respiration and aspirin toxicity should be suspected when both.
Cause is an increase in respiratory rate or volume (hyperventilation) or both. Compensatory metabolic alkalosis (due to chronic respiratory acidosis) should usually be left alone. Ph may be high or near normal.